Difference between revisions of "Modding"
(→Summertime Saga API: Mooooore cleaning and Lesssss typos) |
(Moar cleaning) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{AlertInfo|This page was last updated as of Summertime Saga v0.18.0}} | + | {{AlertInfo|This page was last updated as of Summertime Saga v0.18.0.}} |
= Summertime Saga API = | = Summertime Saga API = | ||
| Line 447: | Line 447: | ||
= Hooking into the game = | = Hooking into the game = | ||
| − | {{AlertWarn|This feature | + | {{AlertWarn|This feature is incomplete as of version 0.18.0, the ModManager class is present, but no hooking of any kind can be done at the moment.}} |
== Registration and enabling of the mod == | == Registration and enabling of the mod == | ||
| − | In an init -9 python or later, use the class method "register" of the ModManager class to register your mod to the game. | + | In an init -9 python or later, use the class method "register" of the ModManager class to register your mod to the game. This registration makes the mod show up in the (upcoming) Mods menu on the main menu so the players have the choice to enable or disable the mod for the game. |
| − | This registration | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | ||
| Line 459: | Line 458: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | A manifest file named <code>modname_manifest.json</code> must be added in the <code>scripts/data</code> folder. | |
== Manifest file == | == Manifest file == | ||
| − | The manifest file | + | The manifest file details in which labels the mod should hook into the game, and which screens. It also defines the name of the main function you wish to use to hook into the <code>game.main()</code> function, if any. |
=== Preferred mod load order === | === Preferred mod load order === | ||
| − | Adding a key named load_order to the manifest will allow your mod to be loaded after a specific amount of mods, or before. | + | Adding a key named load_order to the manifest will allow your mod to be loaded after a specific amount of mods, or before.<br> |
| − | The value of this key must be a string leading with either | + | The value of this key must be a string leading with either <code>></code>, <code><</code> or <code>=</code> followed by an integer. Additionally, the values <code>inf</code> and <code>-inf</code> can be used to set the load order as last, and absolutely first. If several mods are defined with <code>-inf</code> in <code>load_order</code>, then a random order is chosen. The default value is <code>inf</code>, which means the mods are added last to the list in no particular order. |
=== Main function name === | === Main function name === | ||
| − | This key should be a string containing the name of the main function of your mod. The function | + | This key should be a string containing the name of the main function of your mod. The function is searched for ini the <code>globals()</code> of the game (global namespace) |
=== Init label name === | === Init label name === | ||
| − | This key should give the name of a label your mod uses at init time, which means after the game fully | + | This key should give the name of a label your mod uses at init time, which means after the game is fully initialized, either at the start of the game or after the load of the game.<br> |
| − | |||
This label is called in a new context, and it must return, otherwise other mods won't be loaded | This label is called in a new context, and it must return, otherwise other mods won't be loaded | ||
=== Adding to the game's json files === | === Adding to the game's json files === | ||
| − | Keys in the manifest named <code>items</code>, <code>achievements</code> and <code>text_messages</code> can be used to add data to the game's json files. | + | Keys in the manifest named <code>items</code>, <code>achievements</code> and <code>text_messages</code> can be used to add data to the game's json files. Each of these keys expects a full json dictionary formatted in the same way as their respective models. |
| − | Each of these keys expects a full json dictionary | ||
=== Example of a manifest === | === Example of a manifest === | ||
| Line 525: | Line 522: | ||
== Mod init order == | == Mod init order == | ||
| − | {{AlertInfo|Mods are assumed to be in an initial random order}} | + | {{AlertInfo|Mods are assumed to be in an initial random order.}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Finally, update the game's stores (ie achievements, items and text_messages) with every mod's data. Updates overwrite the keys, so the load order can be used to overwrite the game's (although ill‐advised) or another mod's items/text_messages/achievements. | + | For every mod that is enabled, create a Mod instance with that mod's name, parse the load order from the manifest, then insert that mod in the <code>ModManager.mods list</code> in the proper position. Then, for every mod in the <code>ModManager.mods</code> list, call their init label, if defined. Finally, update the game's stores (ie achievements, items and text_messages) with every mod's data. Updates overwrite the keys, so the load order can be used to overwrite the game's (although ill‐advised) or another mod's items/text_messages/achievements. |
== Text filter == | == Text filter == | ||
| − | + | The '''text filter''' key in the manifest allows you to create your own filter function without overwriting other mods. | |
| − | If undefined, this | + | If undefined, this defaults to <code>lambda text:text</code>, otherwise the value of this key should be a string of the name of the function you wish to pass in as a text filter. If the function cannot be found in the global namespace (i.e. the <code>globals()</code> dictionary), then a <code>ModLoaderError("No Function named {text_filter} found in the global namespace. Is it defined properly?")</code> exception will be raised. |
== Screens == | == Screens == | ||
| − | {{AlertInfo| | + | {{AlertInfo|This code is not yet implemented.}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | To add the proper background, start with the statement <code>add player.location.background</code>, which | + | Create your '''screens''' with the following convention : <code>modname</code> + <code>_</code> + <code>in‐game screen name</code> (the Ren'Py definition name). Screens are being included into the main game screens with the use statement. If you wish to add new locations, you have to define a screen for it, in which case, you can inspire yourself with the existing screens in the game.<br> |
| + | To add the proper background, start with the statement <code>add player.location.background</code>, which automatically shows the proper background according to the time of day/period of the year. You can then add imagebuttons. Please refer to the [[#User-defined screen actions|user‐defined screen actions]] for more information on which screen actions the game defines. | ||
== Labels == | == Labels == | ||
| − | {{AlertInfo| | + | {{AlertInfo|This code is not yet implemented.}} |
| − | Only "main" labels can be hooked into. Those are labels that end in <code>$ game.main()</code>. | + | Only "main" '''labels''' can be hooked into. Those are labels that end in <code>$ game.main()</code>. |
== Main function == | == Main function == | ||
| − | {{AlertInfo| | + | {{AlertInfo|This code is not yet implemented.}} |
| − | To hook into the main function, you must register your main function to the ModManager. | + | To hook into the '''main function''', you must register your main function to the ModManager. |
<syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | ||
| Line 564: | Line 555: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | In the above example, <code>ikarumod_main</code> is assumed to be a callable, which should be a python function. This function | + | In the above example, <code>ikarumod_main</code> is assumed to be a callable, which should be a python function. This function is called with no arguments at the end of <code>game.main()</code> method. |
Hooking into the main function is usually useful for code you want executed every time the game returns to a main screen, i.e. at the end of location labels for instance. This is where you can repeatedly check if the condition for an achievement has been fulfilled. If the provided function is not a callable, a ModLoaderError exception will be raised. | Hooking into the main function is usually useful for code you want executed every time the game returns to a main screen, i.e. at the end of location labels for instance. This is where you can repeatedly check if the condition for an achievement has been fulfilled. If the provided function is not a callable, a ModLoaderError exception will be raised. | ||
| Line 636: | Line 627: | ||
== Label calling in the game == | == Label calling in the game == | ||
| − | The game | + | The game offers a function in the Game class to select different dialogues based on the language class attribute defined there. To change that attribute, it's just a matter of writing this piece of code in a separate ".rpy" file. |
<syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Python"> | ||
| Line 643: | Line 634: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | Every time a dialogue is called, the game looks for the label name and the language string at the end. For instance, the label <code>bank_liu_account_info</code> has the | + | Every time a dialogue is called, the game looks for the label name and the language string at the end. For instance, the label <code>bank_liu_account_info</code> has the English version in; and to overwrite that dialogue, you'd have <code>bank_liu_account_info_fr</code> or <code>bank_liu_account_info_es</code> depending on the value of the language string. |
| − | + | Any dialogue can be translated with this method. Keeping a consistent directory structure is recommended, because of the large number of dialogues in the game. You also have to copy over the posing. For your convenience, every dialogue label is stored in a <code>dialogues.rpy</code> file for that location. Just copy the file and edit the dialogue and the label name. | |
== Cutscenes and minigame instructions == | == Cutscenes and minigame instructions == | ||
| − | + | You can't edit the '''cutscenes''' directly. Well, you could, but you shouldn't! Using the <code>config.say_menu_text_filter</code> variable is the best way. Just register a function to that variable with one argument, <code>text</code>, which contains the text of the displayable. Then edit the text how you see fit. | |
<u>'''Example of translation:'''</u> | <u>'''Example of translation:'''</u> | ||
| Line 666: | Line 657: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | Keep in mind however that Ren'Py engine | + | Keep in mind however that Ren'Py engine doesn't handle large dictionaries. <code>elif</code> statements can be used to split the content into several dictionaries if necessary. |
<u>'''Example:'''</u> | <u>'''Example:'''</u> | ||
| Line 693: | Line 684: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | This | + | This allows renaming and translation of any game location, thus displaying that name in relevant parts of the user interface. |
Revision as of 17:35, 14 May 2019
Contents
Summertime Saga API
FSMs (Finite State Machines)
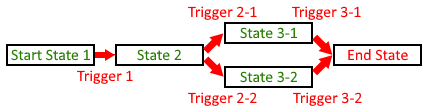
Finite State Machines control the flow of the game for a particular character. They are basically linked chains of events (which are called States). The progress is achieved via a Trigger.
Creating a FSM
Creating a FSM is done in 3 steps:
- Create the states, triggers and a machine instance, providing the necessary arguments to each constructor. Triggers should be created in an init python block of priority 0 or later.
- Link the states together with
State.add(Trigger t, State next_state)method. - Add all the states to the machine with
Machine.add(*State states)method.
State and machine definition and state linking should be done in a label named character_fsm_init, with character being the character's name. Additionally, further edits to the machine (such as adding the states) should be done in a label named character_machine_init, with character being the name of the character.
Machine specific
The machine constructor has plenty of arguments, here is the detail and what is expected:
- name
- A name for the machine used as a unique identifier for the machine. It's also used to find the button dialogue for that machine.
- default_loc
- A 4x7 matrix of locations to be used as the schedule for where a given machine should be at any point during the week. A 4x1 or 2x4 matrix may be passed as well, and internally will be converted to a 4x7 matrix. If a 1x4 matrix is passed, it's assumed that the location only varies by time of day, and the day of the week doesn't matter. A 2x4 matrix will split the two, the first 4-list is for weekdays, and the second for weekend days.
- description, states
- (to be deprecated) An alternate ways to add states to the machine, and a description that is never used anywhere.
- vars
- A dictionary containing variables (as strings, the keys of that dictionary), and init values for those variables. These variables are used with the state actions and the
get(string variable)andset(string variable, object value)methods of the machine class. When a specific state doesn't apply, or you need a variable to change based on the progress with a given path. Thesex speedvariable is assumed to be used only for setting the speed of the animation for sex scenes.
The machine class defines a lot of useful methods:
- set_priority(int priority)
- Set the priority of the machine. Currently used to display the hints on the phone. A machine with a
priorityof 1 or more will show up in the phone. Later, this may be used to sort quests into main quests and side quests. - property button_dialogue
- Return the button dialogue for that machine (
machine name+_button_dialogue), used in the TalkTo screen action. - image, show, say, and hide
- Now defunct methods.
- property progress
- Return an integer that is the progress out of a 100%.
- add_action(*actions)
- Add a machine action to this machine.
- set_state(State state, bool null_delay=False)
- Revert the machine to init, then advance the machine until it is in the state
state. Ifnull_delayisTrue, set the delay of the state reached to 0. - machine_trigger
- Trigger for machine actions.
- trigger(Trigger trigger, bool noactions=False)
- Trigger the machine to pass onto the next state. If
noactionsisTrue, don't process the actions. - add(State* states)
- Add the states to the machine.
- get(string var)
- Get the machine variable
var. - set(string var, object value)
- Set the machine variable
var. - get_state()
- Return the state the machine is in.
- property where
- Compute where the machine should be based on her default location, time of day, day of the week, forced location and if it's forced or not for that time of day. Return a location.
- is_state(State* states)
- Return boolean if the machine is in any of the provided states.
- between_states(State stateBegin, State* statesEnd)
- Return boolean if the machine is between
stateBeginand any of thestatesEnd(non‐inclusive). - finished_state(State* states)
- Return boolean if the machine has finished any of the states provided.
State specific
You may want to add a delay to state creation by using the delay optional argument. That delay is the number of days until that state is effectively reached once the trigger has been "pulled".
When linking states together, you may want to add state actions to be executed when the state is triggered. Those actions are:
- ['set','flag_1']
- Set the value of
flag_1toTrue. - ['clear','flag_1']
- Set the value of
flag_1toFalse. - ['toggle','flag_1']
- Toggle the value of
flag_1betweenTrueandFalse. - ['assign',['v1',100]]
- Set the value of
v1to 100. - ['inc','v1']
- Increase the value of
v1by 1. - ['dec','v1']
- Decrease the value of
v1by 1. - ['triggeronzero':['v1',T_a_trigger]]
- Set
v1 -= 1, and fire the triggerT_a_triggerifv1is less than or equal to 0. - ['trigger',T_a_trigger]
- Fire the trigger
T_a_trigger. - ['call','label']
- Make a Ren'Py call to label. Label MUST return.
- ['location', [machine, {"tod":tod, "place":place}]]
- Set the forced location for the machine to place (moves the non‐player character).
todis 1‐indexed (1 is morning, 2 is afternoon, 3 is evening, 4 is night).- ['force', [machine, {"tod": list or int, "flag": 4-list or bool}]]
- Say if the location is forced at tod or sets force flags according to the 4-list provided.
- ['unforce', None/machine]
- Reset the locations for machine or the machine specified forced.
- ['exec', callable]
- Call the callable function or method.
- ['exec', [callable, *args]]
- Call the callable and pass in the arguments
argsspecified. - ['condition', [condition_string, actions_list_true, actions_list_false, (optional) machine]]
- Execute the actions in
actions_list_trueifcondition_stringevaluates toTrue, otherwise executesactions_list_false. Conditions lists are assumed to be state actions. - ['action', [target_machine, action, target]]
- Execute the state action on another machine.
- ['setdefaultloc', [[Location, Location, Location, Location]]]
- Set the default locations for the current machine.
- The argument is in the same format as the
default_locargument in the machine constructor (1x4, 2x4 or 7x4 matrices). - ['setoutfit', [location, outfit]]
- Set the outfit for that location.
outfitmay be either a string, or a 1x4, 2x4, 7x4 array of strings (similar to the locations). - ['setnaked', True/False]
- Set
is_nakedattribute of the outfit manager toTrue/Falsefor the current machine. - ['setdefaultoutfit', [outfit, {'tod':tod, 'dow':dow}]]
- Set the default outfit for the current machine.
todanddowcan be omitted.outfitis a required argument, can be a string or a 1x4, 2x4, 7x4 matrix.- If
todanddoware omitted,outfitcannot be a matrix, but only a string. A workaround solution exists by passing the{"tod":None, "dow":None}dictionary.
Editing an FSM
Editing an existing FSM is as simple as calling the clear() method of the state you want to clear. It takes one argument, cleardelay, which defaults to False. If cleardelay is True, then the delay of the state is cleared. If you don't want to edit the state, but just want to clear the delay, you can just set the State.delay attribute to 0 instead.
Once cleared, the state is unlinked to the FSM, which means that story will block at that state. It's up to you to link that state to the rest of the machine, with additional states in the middle for your code.
Using FSMs
Using FSMs is surprisingly easy. In the location labels, the machine state can be tested with is_state(State* states) method. Multiple states may be passed in that method, as well as a list of states. If the machine is in any of the provided states, then the method returns True, and False otherwise. For convenience, similar methods can be used: between_states(State state1, State state2) returns True if the machine is in any state between state1 and state2 but is not in state state2; finished_state(State* states) returns True if the machine has finished any of the provided states.
To advance to the next state, trigger(Trigger t) method of the machine class is used. It moves the machine to the next state associated with that trigger if the provided trigger is in the current state table, and doesn't do anything otherwise.
Example of FSM
init python:
T_cassie_ban_mc = Trigger("ban mc")
T_cassie_lift_ban = Trigger("lift ban")
T_cassie_drowning = Trigger("drowning")
T_cassie_end = Trigger("end")
label cassie_fsm_init:
python:
# Cassie's States
S_cassie_start = State("start")
S_cassie_ban_from_pool = State("ban from pool", "You should go to the pool at night...")
S_cassie_caught_skinny_dipping = State("caught skinny dipping", "Cassie lifted your ban! Go for a swim!")
S_cassie_medic_room = State("medic room", "Have fun in the medic room...")
S_cassie_end = State("end")
# Build out Cassie's FSM
S_cassie_start.add(T_cassie_ban_mc, S_cassie_ban_from_pool)
S_cassie_ban_from_pool.add(T_cassie_lift_ban, S_cassie_caught_skinny_dipping)
S_cassie_caught_skinny_dipping.add(T_cassie_drowning, S_cassie_medic_room)
S_cassie_medic_room.add(T_cassie_end, S_cassie_end, actions=["exec", A_drowning_in_pussy.unlock])
M_cassie.add(S_cassie_start, S_cassie_ban_from_pool,
S_cassie_caught_skinny_dipping,
S_cassie_medic_room, S_cassie_end)
return
label cassie_machine_init:
python:
M_cassie = Machine("cassie", default_loc=[[L_pool, L_pool, L_pool, L_NULL]],
vars={'sex speed': .3,
'had sex': False},
)
return
At init time, all the triggers are created. It's important that triggers be created at an init time of 0 or later, since the Trigger class is defined in an init -2 python block, and other parts of FSMs in an init -1 python block.
On starting the game, and on loading a save file or reloading the game, the states are created and linked together, but after the machine itself is initialized. Here is the order applies to the previous example:
cassie_machine_init > call cassie_fsm_initExplication: the machine is named M_cassie and is given the name cassie. This name is used in several places throughout the code to refer to that object. Furthermore, Cassie's default location (default_loc argument) specifies that the character is at the pool from morning to evening, and nowhere in the night. A dictionary is initialized as well to keep track of some other variables, like the sex animations speed, the previous sexual interactions with that character, the variables to trigger repeatable dialogues, counters, etc.
In the same label, you can set up the outfit system of that character, as seen in the next section, or add machine actions to the FSM. This is also the place to set the priority of the FSM.
The states are created and linked in the label cassie_fsm_init. In the given example, the last link has a state action attached to it, which means that on reaching the S_cassie_end state, the machine automatically calls the unlock method of the A_drowning_in_pussy achievement. In the same way, other state actions may be defined.
More examples:
S_diane_drunken_splur.add(T_diane_help_carry_to_bed, S_diane_get_cold_towel,
actions = ["location", {"place": L_diane_bedroom},
"force", {"tod": [0,1]},
]
)
S_diane_milking_help.add(T_diane_milking_malfunction_help, S_diane_debbie_evening_visit,
actions = ["location", {"place": L_home_kitchen,
"condition": "not M_diane.is_set('first cucumber')",
},
"force", {"tod": 2},
]
)
S_diane_look_in_kitchen.add(T_diane_search_kitchen, S_diane_seen_cucumber,
actions = ["action", [M_player, "set", "jerk diane"]
]
)
S_diane_fetch_pump.add(T_diane_found_pump, S_diane_delivery_2_task,
actions = ["setdefaultloc", [[L_diane_shed, L_diane_shed, L_diane_shed, L_diane_bedroom]]]
)
Outfit manager
Every FSM has an outfit manager instance attached to it. This system is designed a bit like the Location system: each outfit has a specific time of day/day of week schedule for which the character is wearing that outfit. The manager also considers the current location and handles whether the character is naked or not, with the is_naked attribute.
To bind the schedule of an outfit to a specific location, use the method bind_outfit_to_location, with the location as first argument, and the outfit string/schedule as second argument.
An outfit schedule is very similar to a location schedule, it's a 1x4/2x4/7x4 matrix of strings, each of those strings being the outfit of a given pair of time of day/day of week.
Init arguments:
- default_outfit
- Defaults to
[["dressed", "dressed", "dressed", "dressed"]]. - is_naked
- Defaults to
False.
Methods and attributes:
- default_outfit
- The outfit schedule used if the character is in a location that doesn't have a table of outfits for that character.
- is_naked
- Boolean that tells if the machine is naked or not.
- bind_outfit_to_location(Location location, object outfit_schedule)
- Bind the given outfit schedule to the given location. The outfit schedule may be a string, a 1x4 matrix, a 2x4 matrix or a 7x4 matrix of strings.
- format_outfit_schedule(object outfit_schedule)
- Format the outfit schedule to a 7x4 matrix of strings. Used internally.
- property get()
- Return the proper outfit given the current time of day, day of week, whether the machine is naked or not, and current location.
So basically how the new outfit system works
you have to setup the outfit manager. The outfit manager has one method called bind_outfit_to_location that takes 2 arguments : location, a location object, and outfit, which can be an outfit string or an outfit schedule, i.e. a matrix just like the locations)
so what you do is use that method to create basically a map of outfits to use in certain conditions
moreover, outfits can be set with a simple state action, which takes care of calling the bind_outfit_to_location method
also, now, to get the outfit, it's as simple as calling M_diane.outfit.get
(without any parentheses, get is a property of the outfit manager)
the is_naked variable has also been moved to the outfit manager, because it's cleaner
instead of M_diane.get_naked_str, you use M_diane.outfit.get
instead of doing M_diane.outfit = "whatever" you must configure the outfit manager
M_diane.outfit.bind_outfit_to_location(L_home_livingroom, "casual")
if you want more granularity, you can do this
M_diane.outfit.bind_outfit_to_location(L_home_livingroom, [["dressed", "dressed", "casual", "casual"]])
you can even set that matrix to bean individual outfit for each time of day, each day of the week
as for the state action, there is setnaked and setoutfit
setnaked will set the machine to be naked or not, thing you can also do with M_diane.outfit.is_naked = True / False
True /False not True over False, it's not a division
and setoutfit just calls bind_outfit_to_location method with the two arguments you specify, like so
actions=["setoutfit", [L_home_livingroom, "casual"]]
the Machine.outfit.get property works like that:
if the machine is naked
return "naked"
otherwise if the player is in a location the outfit manager is not bound to
if the outfit to be returned is "naked", set the is_naked attribute to True, and False otherwise
return default_outfit for that day of week and time of day
otherwise
if the outfit to be returned is "naked", set the is_naked attribute to True, and False otherwise
return outfit for that location at that day of week and time of day
Use del M_diane.outfit.outfits[L_home_livingroom] to revert back to the default if needed.
Pregnancy manager
Locations
Locations handle all the locations in the game. They are represented as a tree, with the possibility of multiple parents (like Smith's Bedroom, which has the front yard and the hallway as its parents). A required attribute is the location name.
Creating a location
Locations are easy to create. It's as simple as instantiating the Location class, and providing a name for that location to the constructor (which is the only required argument). Locations are mutable, so they should be instantiated in a modname_locations_init label.
Furthermore, a locations has several optional arguments:
- name
- The name for that location, as can be seen in the top‐left corner of the screen. It's also the way to find and call the relevant location screen, as well as the location label.
- unlock_popup
- The name of a Ren'Py‐defined displayable for the popup that should show up when the location is unlocked.
- background
- The name of the background used for that location. The background name must follow several conventions to properly work:
- Must be in the folder
images/backgrounds/ - Name must start with
location_ - Name must end with
_day.jpg,_evening.jpgor_night.jpg, respectively for day, evening or night background. - For Halloween or Christmas backgrounds, the strings
_halloweenand_christmasmust be added before the time of day code. This will allow the game to find relevant backgrounds for the time period.
- Must be in the folder
- Whatever is leftover should be provided in the background argument of the constructor. The full file path will be constructed by the background (resp.
background_blur) properties. - parents
- Either a list of location or a single location instance. Provide the parents of that location. If left empty, the location is assumed to be the root of the tree. The root should always be
L_map(orL_NULL, butL_NULLshould not have children). - locked
- Defaults to
False. Whether that location should be initially locked, and inaccessible at the beginning of the game. - label
- (to be deprecated) The label name for that location.
formatted_nameproperty will be used later on.
Example:
L_diane_barn = Location("Diane's Barn", unlock_popup="popup_diane_barn", background="barn_frontyard", parents=L_map, locked=True)
This code defines a location named "Diane's Barn" (formatted name: dianes_barn), child of L_map, that shows popup_diane_barn on unlock, and that is initially locked. The background is set as barn_frontyard, which means the game looks for files named backgrounds/location_barn_frontyard_day.jpg or backgrounds/location_barn_frontyard_night.jpg for instance.
User‐defined screen actions
The screen actions are specific to Summertime Saga and should be used to keep the flow consistent.
MoveTo
This action expects a location to be passed. It hides the current screen, moves the player to that location, and calls the corresponding screen as well as jumps to the location label.
BuyItem
This action expects an item, or item identifier string to be passed to it. When activated, buys the item, and shows the appropriate failing popups should the transaction fail. Optionally, you may add a callback label with the callback_label optional argument. If the transaction succeeds, the game then calls that label. Useful if you want some story element to trigger after buying an item.
TalkTo
This action is used to talk to the character. It hides the screen and start the conversation with the given character. It expects a machine instance, or a string to identify it, in which case it attempts to find the machine in the store.machines dictionary.
ClearPersistent
This action resets all persistent data (cookie jar, time spent playing, achievements etc). No arguments expected.
GetItem
Ths action gets the item, and attempts to show the corresponding popup. No arguments required.
JSON Data
Items and inventory management
The inventory manager is fully automatic, but you may want to add some items to the game. Items are stored in items.json file located in scripts/data/folder.
Example:
"birth_control_pills": {
"id": "173",
"name": "{b}Birth Control Pills:{/b}",
"cost": "0",
"image": "objects/item_pills3.png",
"description": "Makes you temporarily sterile.",
"closeup": "",
"dialogue_label": "birth_control_pills",
"popup_image": ""
}
In order:
birth_control_pills: the item identifier.id: a numeric id. Unused at this moment.name: the item name, as seen in the inventory.cost: the item cost. It's cast as an integer, and prevents the player from picking up the item if he doesn't have sufficient money.image: the item miniature image, as seen in the inventory.description: the item description, as seen in the inventory.closeup: the item close‐up image, if there is one.dialogue_label: the item dialogue label. It's triggered if it exists, on clicking the item. The label should always return, and take an item argument.popup_image: the item popup image. It's displayed when first acquiring the item, leave the string empty if there is none.
Text messages
Text messages are stored in this format in text_messages.json file. Once defined there, you can use player.receive_message(message_id) for the player to receive the message.
Example:
"mia02": {
"sender": "mia",
"content_preview": "We can't find {b}my dad{/b}...",
"content": "We can't find {b}my dad{/b}...\nCan you come help us please?",
"image": "cellphone/cellphone_text_mia01.png"
}
In order:
mia02: the message identifier. Must be unique. Message identifiers ending in_pregnancyor_pregnancy_laborare reserved for the pregnancy system messages.sender: the name of the machine that sent this message.content_preview: the preview text displayed on the phone main screen.content: the actual message displayed when clicking the message in the phone.image: the image used as a "profile picture on the phone.
Achievements
Achievements are defined in achievements.json file.
Example:
"angler": {
"id": 1,
"name": "The Angler",
"description": "Catch one of every type of fish.",
"hidden": false,
"enabled": true,
"image": "achievements/cellphone_achieve_01.png"
}
In order:
angler: the achievement identifier. Must be unique. The identifier is used to name the achievement variable. Dashes are replaced with underscores. All achievements are prefixed with "A_".id: a numeric id. Unused.name: the achievement's name.description: the achievement's description. New lines are inserted every 30 characters, words are not split in the middle.hidden: whether it's a secret achievement or not.enabled: if the achievement can be achieved.image: the icon for this achievement.
Dialogues
The dialogues.json file is used for the dialogue lines written by patrons.
Key binding
This file lists the default key bindings used by the minigames.
Furnishings
This file will be similar to items.json. At the moment, no furnishings have been implemented. Thet will be available for the beach house location and will include an upgrade system.
Game manager class
The game manager class handles everything that is related to the gameplay itself, but is not planned to be extendable by mods. Its methods and attributes are still usable and should be used for your mod.
- language
- Set the language of the game which is used for translations. Defaults to
"en"for English with other languages in the game untranslated. - cheat_mode
- Return
Trueif the game is currently in cheat mode (thus allowing minigames to be skipped). - CA_FILE
- Path to a certification file used to enable requests to websites. Used only if the player has checked the option "allow internet connection".
- lock_ui()
- Lock the user interface.
- unlock_ui()
- Unlock the user interface.
- ui_locked()
- Return whether the user interface is locked or not (i.e. grayed‐out).
- dialog_select(string label_name)
- Classmethod that chooses a label based on its name and the language class attribute. To be used to split dialogues and logic, and also allows your mod to be easily translated.
- choose_label(string template)
- Classmethod that chooses a label at random that matches the template passed in the arguments.
- main()
- Method that is to be called at the end of every label the player jumps to (and not called to). It calls the player's location screen, and checks for achievements and other stuff. This would be the only method expandable upon. It also clears the return stack, so that traceback are not indigestible. It may take two arguments,
clear_return_stackto enable or not return stack clearing, and location, to call the screen of another location than the player's currently in. - is_christmas()
- Classmethods that checks if the system clock matches Christmas.
- is_halloween()
- Classmethods that checks if the system clock matches Halloween.
Player class
The player class handles everything related to the player: the inventory, grades, vehicle level and stats. Notable methods:
- receive_message(string message_id)
- Check if the player has received the given text message on the phone. Also sets up the alert icon on the user interface.
- has_item(string* items)
- Check if the player has any of the items provided at this moment.
- has_picked_up_item(string* items)
- Check if the player has ever picked up any of the items provided.
- get_item(string item)
- Get the item if the price of the item doesn't exceed the amount of the player's money.
- remove_item(string item)
- Remove an item by its string id.
- get_money(int money)
- Add money to the player.
- spend_money(int money)
- Subtract money from the player.
- has_required_str(int min_str)
- Check if the player has the required strength. Similar method exist for
int,chranddex. - go_to(Location location)
- Go to the given location.
- go_to_previous()
- Go to the first parent location of the current location.
- increase_str(int amount)
- Increase the strength by amount. Defaults to 1. Similar method exist for
int,chranddex.
Miscellaneous functions and classes
- KeepRefs
- A class used everywhere to make sure to keep a reference to any object instantiated, making sure is checks are kept correct.
- get_instances()
- Classmethod to get a generator of all the instances of this class subclass.
- LastUpdatedOrderedDict
- A dictionary‐like structure that keeps its order, and store its items in the order the keys were last added (and not updated). This is a subclass of Python's OrderedDict from the collections package.
- listvalues
- Return a list of all the values of this dictionary.
- listkeys
- Return a list of all the keys of this dictionary.
- lastkey
- Return the last key added to this dictionary.
- lastvalue
- Return the value of the last key added to this dictionary.
- isempty
- Return whether the dictionary is empty.
- format_seconds_to_dhm(int seconds)
- Return a formatted string in the form (x)d (y)h (z)m from the number of seconds passed in the arguments.
- insert_newlines(string string_to_format, int every)
- Return a new string based on the passed in string, with newlines inserted every
everycharacter.everydefaults to 30. Differs fromsplice_string()in that it is not cut a word in the middle if possible.splice_string()inserts a newline everyeverycharacters without question.insert_newline()is much safer as it will not cut a variable substitution, but is much slower thansplice_string().
- text_identity(string text)
- Return unmodified text, useful for
config.say_menu_text_filterif it isNone.
- replace_bracket(string text)
- Return text without the [ and ] characters (Ren'Py variable formatting syntax).
- gauss(float mean, float deviation, float lower, float upper)
- Return a random integer number in a normal distribution, clamped between lower and upper.
- get_angle_speeds(int angle_width, Iterator angle_range, Iterator speed_range)
- Return two lists –
true anglesandfalse angles– which are lists of tuples (initial_angle, initial_speed) for which the result land in or out of theangle_width. Used in Pregnancy minigame and Spin the Bottle minigame.
- safe_parse_dict(dict dct, object* keys, object default=None, list list_to_append=None)
- Return the content of the dictionary at keys
keys, subscribed in order. If a KeyError exception is raised, and a default is provided, then will return that default object. Any number of keys can be passed up to 253 (hard limit in CPython). Additionally, you can pass in a list to append the name of the missing keys of the dictionary to.
Examples:
safe_parse_dict({"a":{"b":2}}, "a", "c", default="default return value")
# returns "default return value"
safe_parse_dict({"a":{"b":2}}, "a", "b", default="default return value")
# returns 2
safe_parse_dict({"a":{"b":2}}, "a", "b", "default return value")
# prints "Extra positional argument passed, is default properly named in the arguments?" and returns 2
safe_parse_dict({"a":{"b":2}}, "a", "c", list_to_append=missing_keys)
# appends "c" to list missing keys and returns None. If a default argument is passed, will return default
Hooking into the game
Registration and enabling of the mod
In an init -9 python or later, use the class method "register" of the ModManager class to register your mod to the game. This registration makes the mod show up in the (upcoming) Mods menu on the main menu so the players have the choice to enable or disable the mod for the game.
init python:
ModManager.register("ikarumod")
A manifest file named modname_manifest.json must be added in the scripts/data folder.
Manifest file
The manifest file details in which labels the mod should hook into the game, and which screens. It also defines the name of the main function you wish to use to hook into the game.main() function, if any.
Preferred mod load order
Adding a key named load_order to the manifest will allow your mod to be loaded after a specific amount of mods, or before.
The value of this key must be a string leading with either >, < or = followed by an integer. Additionally, the values inf and -inf can be used to set the load order as last, and absolutely first. If several mods are defined with -inf in load_order, then a random order is chosen. The default value is inf, which means the mods are added last to the list in no particular order.
Main function name
This key should be a string containing the name of the main function of your mod. The function is searched for ini the globals() of the game (global namespace)
Init label name
This key should give the name of a label your mod uses at init time, which means after the game is fully initialized, either at the start of the game or after the load of the game.
This label is called in a new context, and it must return, otherwise other mods won't be loaded
Adding to the game's json files
Keys in the manifest named items, achievements and text_messages can be used to add data to the game's json files. Each of these keys expects a full json dictionary formatted in the same way as their respective models.
Example of a manifest
{
"name":"ikarumod",
"version": "0.1.0",
"load_order": ">3",
"main_function_name": "ikarumod_main",
"init_label_name":"ikarumod_init_label",
"text_filter":"ikarumod_text_filter",
"items": {
"item1":{
...
},
"item2":{
...
}
},
"text_messages":{
"text_message1":{
...
}
},
"screen_hooks":{
"upstairs_bedroom":"upstairs_bedroom_ikarumod",
"bedroom":"bedroom_ikarumod"
},
"label_hooks":{
"bedroom":"bedroom_ikarumod"
},
"achievements":{
"angler-2"{
...
}
}
}
Mod init order
For every mod that is enabled, create a Mod instance with that mod's name, parse the load order from the manifest, then insert that mod in the ModManager.mods list in the proper position. Then, for every mod in the ModManager.mods list, call their init label, if defined. Finally, update the game's stores (ie achievements, items and text_messages) with every mod's data. Updates overwrite the keys, so the load order can be used to overwrite the game's (although ill‐advised) or another mod's items/text_messages/achievements.
Text filter
The text filter key in the manifest allows you to create your own filter function without overwriting other mods.
If undefined, this defaults to lambda text:text, otherwise the value of this key should be a string of the name of the function you wish to pass in as a text filter. If the function cannot be found in the global namespace (i.e. the globals() dictionary), then a ModLoaderError("No Function named {text_filter} found in the global namespace. Is it defined properly?") exception will be raised.
Screens
Create your screens with the following convention : modname + _ + in‐game screen name (the Ren'Py definition name). Screens are being included into the main game screens with the use statement. If you wish to add new locations, you have to define a screen for it, in which case, you can inspire yourself with the existing screens in the game.
To add the proper background, start with the statement add player.location.background, which automatically shows the proper background according to the time of day/period of the year. You can then add imagebuttons. Please refer to the user‐defined screen actions for more information on which screen actions the game defines.
Labels
Only "main" labels can be hooked into. Those are labels that end in $ game.main().
Main function
To hook into the main function, you must register your main function to the ModManager.
init python:
ModManager.register_main(ikarumod_main)
In the above example, ikarumod_main is assumed to be a callable, which should be a python function. This function is called with no arguments at the end of game.main() method.
Hooking into the main function is usually useful for code you want executed every time the game returns to a main screen, i.e. at the end of location labels for instance. This is where you can repeatedly check if the condition for an achievement has been fulfilled. If the provided function is not a callable, a ModLoaderError exception will be raised.
Imported modules and directory structure
Third‐party modules
Platform agnostic
- os
- pygame
- sys
- from time : time, clock
- from copy : copy, deepcopy
- datetime
- re
- random
- math
- from collections : defaultdict, OrderedDict and Counter
- weakref
- codecs
- hashlib
- json
- itertools
- operator
- textwrap
- deuces
Desktop builds
- certifi
- requests
Mobile builds
- android
- pyjnius
Directory structure
gameaudio: SFX and musicsfonts: fonts for the game.imagesachievements: achievement‐related images.cookie_jar: cookie jar buttons, popups and thumbnails.backgrounds: backgrounds and close‐ups.boxes: popups and general purpose buttons (like the go back button).buttons: most minigame assets, and menu buttons.cellphone: cellphone images assets.characters: character poses. One folder per character.map: map locations and map background.objects: character buttons, item buttons, doors, etc.vfx: special visual effects (like the rain in roxxy's trailing scene).
python-packages: third party python modules.scriptscharacters: one folder for each character, containing an fsm file, a character.rpy file for miscellaneous stuff, and a layeredimage definition file. May contain a file for the character's button and the according dialogues.core: core files are put there, mostly what has been documented in the Modding API section of this manifesto.data: JSON files that contain data about the game. Items, achievements, keymap or text messages are defined here.defines: general image definitions, transforms, etc.locations: one folder for every location, sorted in a tree‐like structure. Each location has a main file, a screen file and a dialogues file.minigames: one folder for every minigame, the minigame dialogues and screen files are in that folder.script.rpypregnancy_announcements.rpy
changelog.txtpledge_list.txt
Translating the game
Label calling in the game
The game offers a function in the Game class to select different dialogues based on the language class attribute defined there. To change that attribute, it's just a matter of writing this piece of code in a separate ".rpy" file.
init 1 python:
Game.language = "es" # for Spanish for instance, "fr" for French, etc
Every time a dialogue is called, the game looks for the label name and the language string at the end. For instance, the label bank_liu_account_info has the English version in; and to overwrite that dialogue, you'd have bank_liu_account_info_fr or bank_liu_account_info_es depending on the value of the language string.
Any dialogue can be translated with this method. Keeping a consistent directory structure is recommended, because of the large number of dialogues in the game. You also have to copy over the posing. For your convenience, every dialogue label is stored in a dialogues.rpy file for that location. Just copy the file and edit the dialogue and the label name.
Cutscenes and minigame instructions
You can't edit the cutscenes directly. Well, you could, but you shouldn't! Using the config.say_menu_text_filter variable is the best way. Just register a function to that variable with one argument, text, which contains the text of the displayable. Then edit the text how you see fit.
Example of translation:
init 10 python:
fr_translations = {"Using the key and stool, I was able to get into our attic.\nI had never been up there before.\nI was filled with excitement wondering what treasures {b}[deb_name]{/b} and dad had stashed away.": "En utilisant la clé et le tabouret, je pus aller dans le grenier.\nJe n'y avais jamais été auparavant.\nUn sentiment d'excitation m'envahissait alors que je me demandais quels trésors {b}[deb_name]{/b} et papa avaient caché là-haut."}
def fr_text_filter(text):
if text in fr_translations.keys():
return fr_translations[text]
else:
return text
config.say_menu_text_filter = fr_text_filter
Keep in mind however that Ren'Py engine doesn't handle large dictionaries. elif statements can be used to split the content into several dictionaries if necessary.
Example:
def fr_text_filter(text):
if text in fr_translations_1.keys():
return fr_translations_1[text]
elif text in fr_translations_2.keys():
return fr_translations_2[text]
else:
return text
In the future, registering to config.say_menu_text_filter variable will be done with the += assignment, to allow several mods to subscribe to it. Mod load order will apply.
Location names
In an init 1 python (or later) block, you can set the display name of any location object in the game.
Example:
init -1 python:
L_map.display_name = "New Map Name"
This allows renaming and translation of any game location, thus displaying that name in relevant parts of the user interface.